- Published on
Learn Docker by its key concepts

What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform for building, running and shipping applications. Developers can easily build and deploy applications running in containers. Local development is the same across any environment. Docker solves the problem of creating, deploying, and running applications consistently across different environments by using containerization to package software with all its dependencies.
Why is it better than VM?
Because it uses containerization to achieve greater efficiency, speed, and resource utilization by sharing the host system's kernel and isolating applications in lightweight containers instead of creating separate full operating systems.
Key Concepts
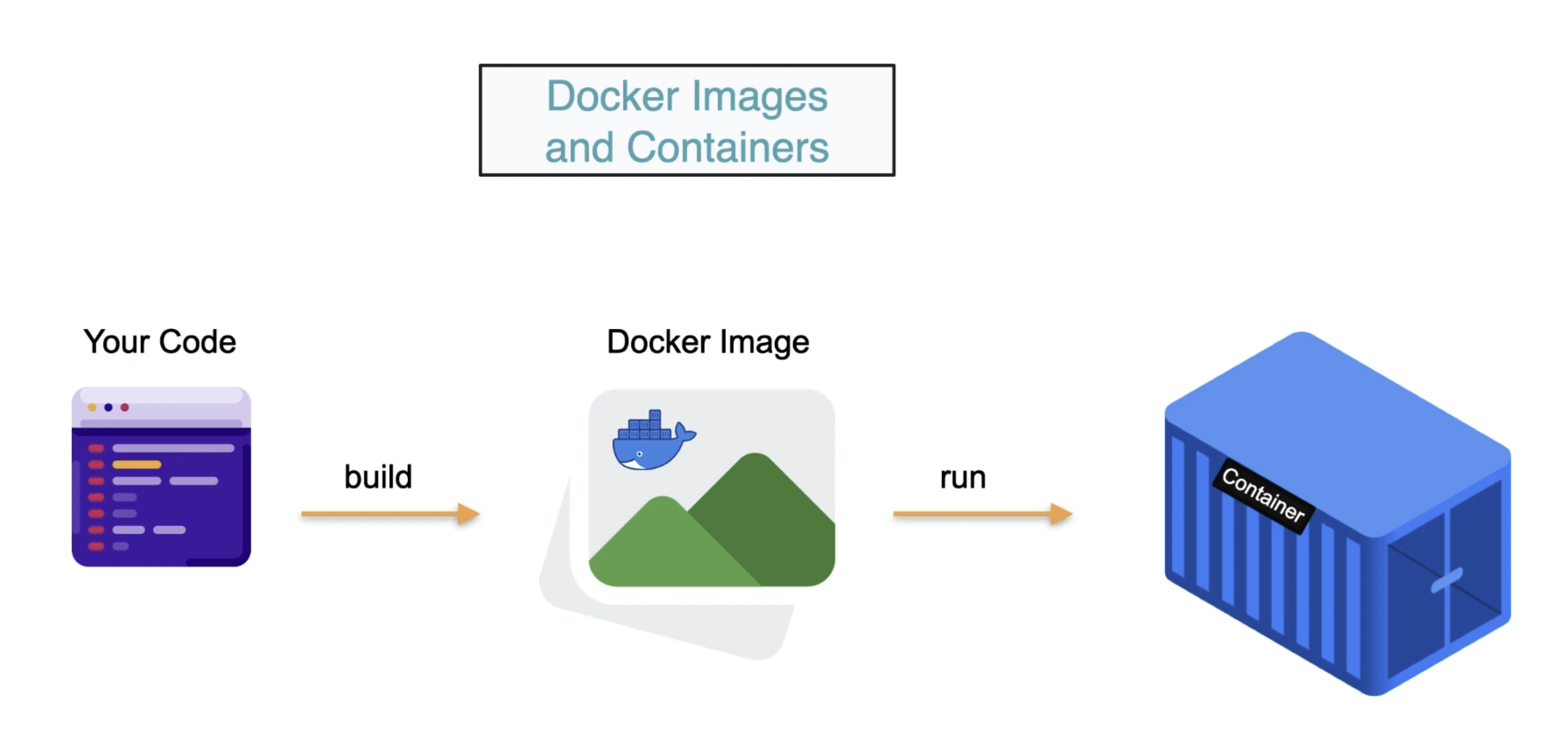
Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a text file containing a series of instructions that define how to build a Docker image, specifying the operating system, application code, dependencies, and configuration. It is used to build a single Docker image by specifying the instructions needed to set up the environment and install the necessary software for your application. It's like a recipe for creating an image.Image
Containers
An isolated environment for running an application.
Docker Architecture(client - server )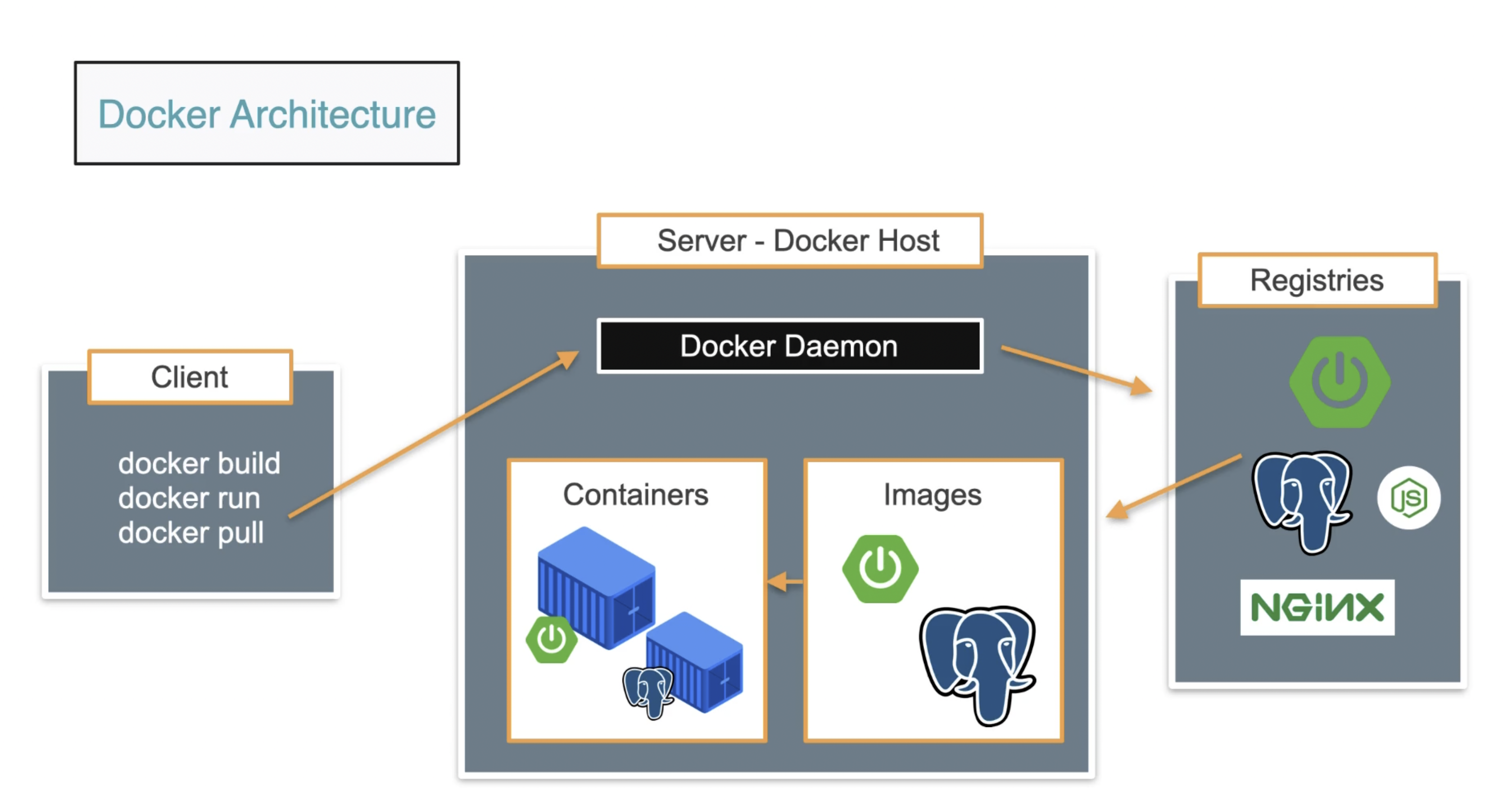
Registries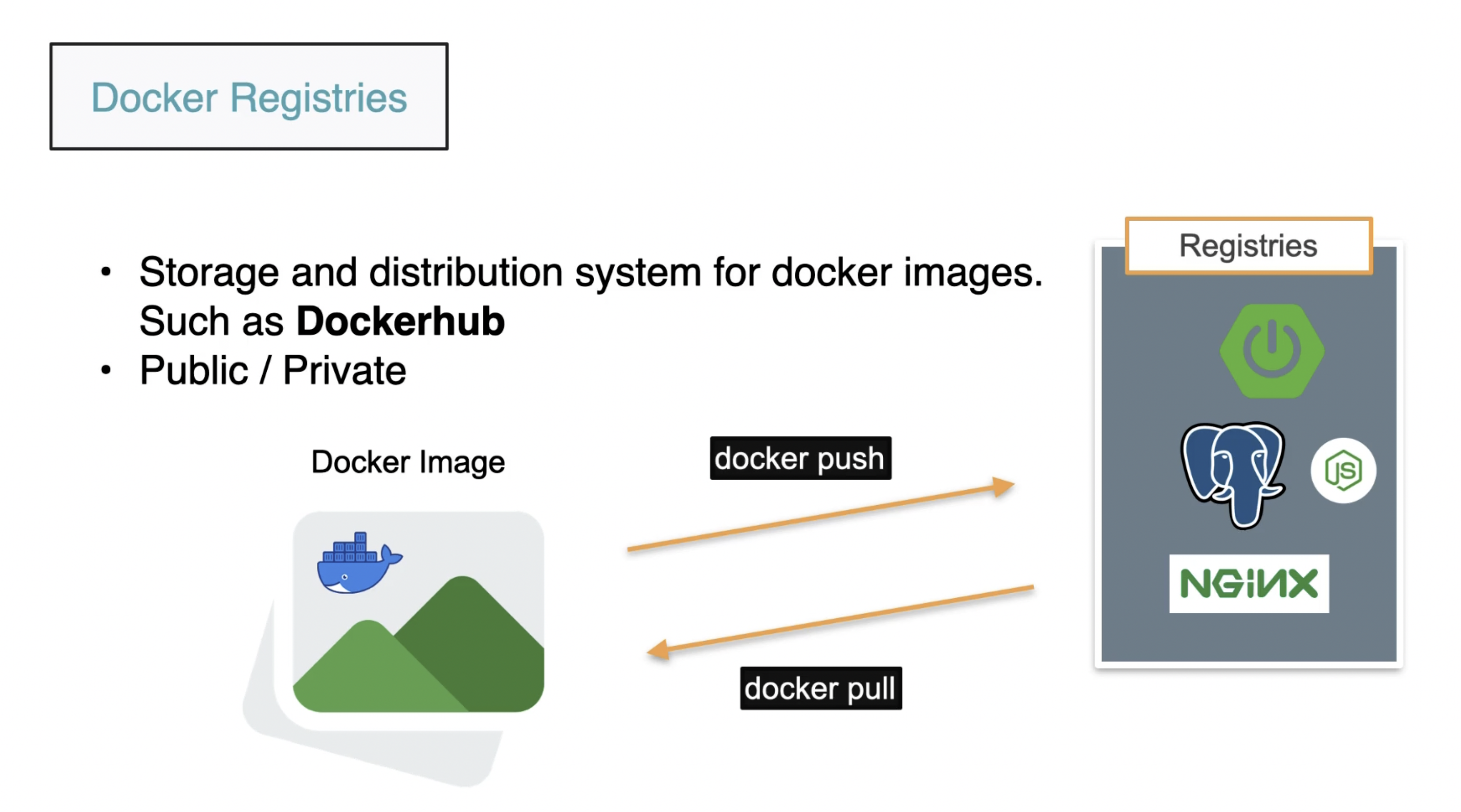
docker-compose.yml
A docker-compose.yml file is used to define and manage multi-container Docker applications. It allows you to specify how multiple containers should work together, including their configuration, networks, and volumes. It orchestrates the running of several services (containers).volumes
In Docker, volumes are a type ofstorage mechanismthat allows data to persist beyond the life of a container. They are managed by Docker and can be used to share data between containers or between the host system and containers. Volumes are the preferred way to handle persistent data in Docker because they offer several advantages, such as easy backup and restore, sharing between multiple containers, and better performance compared to other storage options like bind mounts.)